Do Quotes Count as Duplicate Content in Blog Posts?

Way back in the far-off year of 2010, the internet was packed to the gills with duplicate content. Many times, you would perform a Google search and find that 9 of the top 10 results were different domains, different site designs, but the same content on all of them. Sometimes the only difference would be a different regional keyword for the business trying to use that content to rake in the traffic.
As you can imagine, this made an absolute mess out of search results. It was nearly impossible to get anything worthwhile when researching information. It's no wonder that Google decided to make a change, and that change was the Panda Update.
Among many things Panda hit was duplicate content. Google began tracking when they first saw content appear, and they would penalize sites that copied content after it was originally published. If I wrote an article and you published the same article, and worse, if you make a regular habit of doing this more often than publishing new content, you could potentially be penalized for copying that content (or at the very least, it would not perform as well).

This move pushed originality and is a huge part of why the internet looks the way it does today. It also led to a lot of different problems.
For example, syndication. Plenty of sites, like Yahoo and other news agencies, syndicate content from one another and from a few primary sources. Posts written by the Associated Press or by Reuters are re-posted on hundreds of different news sites. Do those sites eat a penalty for duplicate content?
No, this is no longer the case. They might have for a while, but Google solved the problem by introducing the rel="canonical" tag. This tag is something you can put on a page that is copied from another source, to point to the original source and give credit to that original source. Syndication, though, is a form of copied content that is sanctioned. It's allowed.
 30 Second Summary
30 Second Summary
You'll want to avoid copying large chunks of content when quoting others in your posts. If you use quotes, wrap them in blockquote HTML tags and cite the original source with links or proper attribution. Keep quotes brief - only include what's necessary to make your point. Your own original content should make up most of your post, with quotes serving as supporting elements. When possible, you can rewrite important points in your own words instead of directly quoting them.
Partial Duplicate Content and Quotes
There's also the problem of partial duplicate content. If I were to take three different blog posts and copy the intro from one, the body from another, and the conclusion from the third, is my content original?
The answer is no. Even if I'm synthesizing a new whole from parts of other posts, it's still nothing original. It's not like images, where a collection of content can be more than the sum of its parts.
So this leads us to the question: where do you draw the line?
After all, if you think about it, every blog post on the internet is copied content from the dictionary. It's all just remixes of the order and number of words. Or to put it another way, it's all just the alphabet, rearranged.
For example, taking chunks of other blog posts and publishing them together as a "new" blog post is copied content and won't perform very well. But how much original content do you need? At what point is a quote-heavy post going to be penalized?
Well, how about this. Here's a post from Wishpond that is filled with a series of quotes from various marketers with no original content, other than "click to tweet" links between each one and two sentences of introduction text.
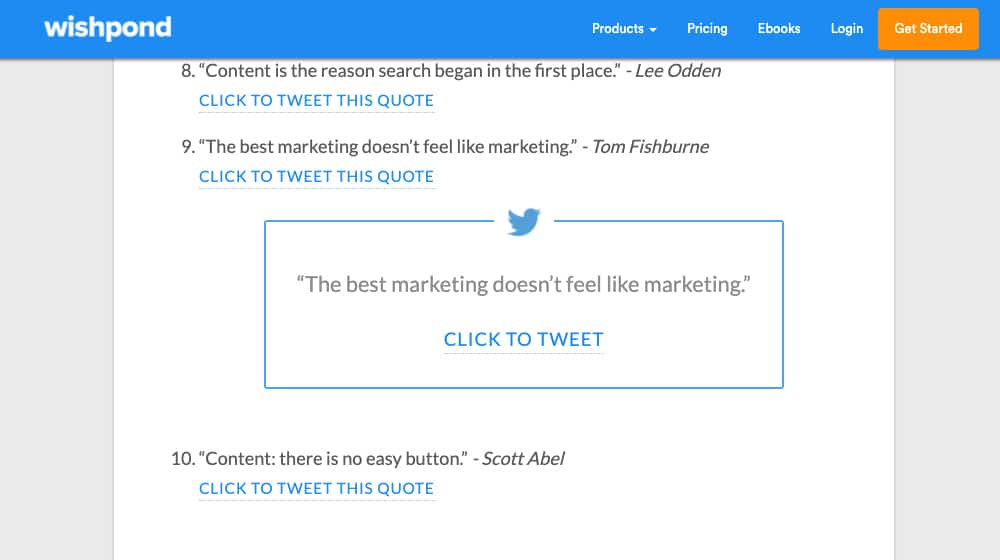
That page isn't demoted by Google; I know because I found it on Google and it was ranking number one for "quotes and advice from marketers". HubSpot has a similar post, with a bit more original content, found here.
Of course, you don't have to take it all from me. Google has an official stance, which Matt Cutts expounded upon in a video back in 2012. You can watch the video here:
What it comes down to is this: add value, whether it's on the rest of your site at large, or throughout the post itself. Make sure your quotes add value to your posts, or your posts add value to your quotes. If you do that, you'll be fine.
So, it's plain to see that quotes won't automatically kill your page or your site because they're duplicate content. How should you handle them, though? Where should you draw the line to get the most value out of quotes, without making your site nothing but quotes? Luckily for you, I have a whole bunch of useful tips.
In modern HTML, there's a tag called blockquote, which is used explicitly for this purpose. You use it to wrap quotations in, and this does several things. You can read about its actual usage here.
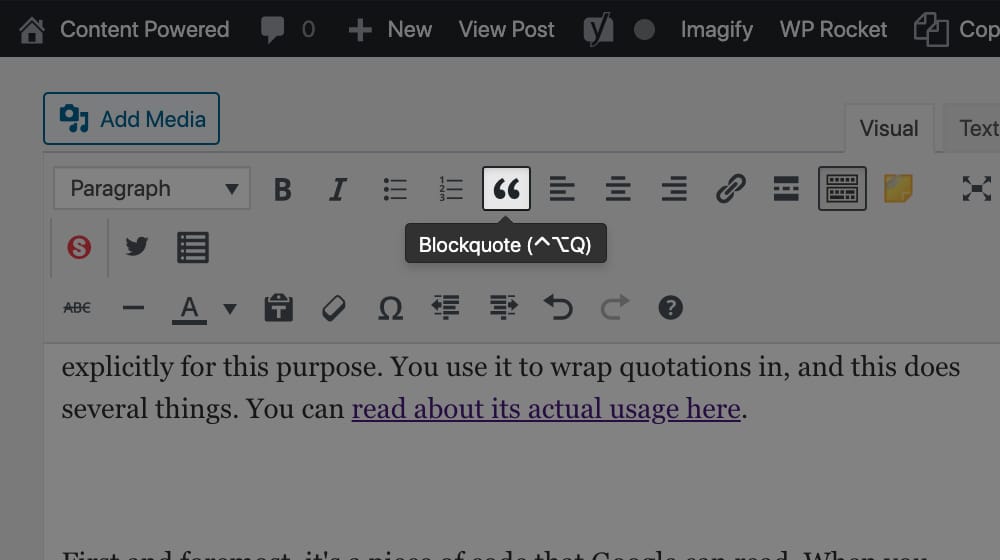
First and foremost, it's a piece of code that Google can read. When you wrap text in the blockquote tag, Google can see it, and they can recognize that you're flagging this text as a quote rather than a piece of text normally in your post. It's not enough to use "quotation marks" around text; you need to use the HTML tag as well.
Secondly, there's an attribute of the blockquote tag called cite. You can use that to cite a URL the quote is from. Note that this only works for URLs; you can't quote a book and cite the book's author in the cite attribute (unless the book is published on a web page). In practice, it looks like this:
<blockquote cite="https://neilpatel.com/blog/myths-about-duplicate-content/"> "I have never seen any evidence that non-original content hurts a site's ranking, except for one truly extreme case." – Andy Crestodina, via NeilPatel.com </blockquote>
Which, when formatted, looks like this:
"I have never seen any evidence that non-original content hurts a site's ranking, except for one truly extreme case." – Andy Crestodina, via NeilPatel.com
Note that the citation link is an attribute of the HTML code, it's not something publicly visible. To add that visible attribution, you also need to have a link there in your text, as I added to the "via NeilPatel.com" bit.
This leads me to the third thing the blockquote tag can do: adding some custom CSS styling, like in my example above. You can style and theme the blockquote block in your site's code to make it look unique and stand out as a quote. I just make mine indented and highlighted with a bit of orange, but I've seen websites put quotation marks in the upper left and lower right corners and add other forms of custom theming on top of it.
With CSS, you can do a lot of wild things, so you might as well play with it, or have your web designer help you out. If it enhances your user experience, it's good for your website.
Quote as Little as Necessary
Duplicate content comes close to brushing up against something in law called copyright. I'll talk more about copyright later, but first, let's mention Fair Use. Fair Use is a copyright defense that allows for uses of copyrighted material in specific situations. Essentially, "even though this is copyrighted, you can use it, so long as you follow specific rules."
Fair Use is a very complicated situation, and figuring it out is what the majority of copyright lawsuits are about. You can read about the factors of Fair Use here.
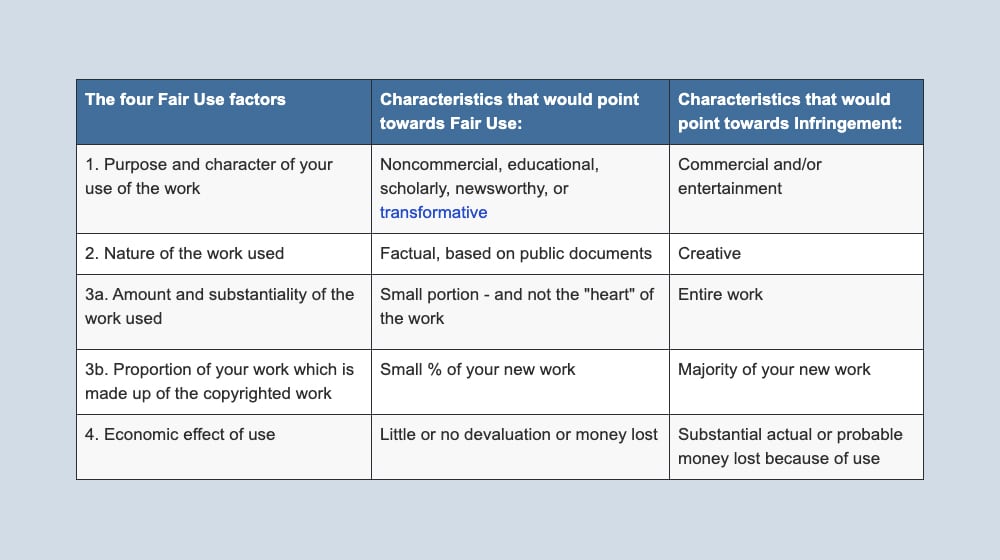
One aspect of Fair Use is how much of the copyrighted work you used. Reproducing an image in full, for example, uses all of the copyrighted work. A YouTube video that cites a 30-second portion of another YouTube video (for the purposes of criticism) uses only a small portion of that other video. One of these is much more likely to be a copyright violation than the other, and I bet you can guess which one.
(It's the image example.)
So, when it comes to text, the amount you quote matters. You can quote long passages! In this post, I quoted three paragraphs from a source. That source was a novel, though, so the amount of the novel I quoted was very minimal compared to the full source. I quoted only the relevant passage, no more, no less.
That's what you should strive to do. Quote exactly as much as is meaningful for your purposes. If you quote more, you're copying more than is necessary. If you quote less, the meaning is lost. It's a line you need to draw, and it does mean you need to figure out just how much of the passage you need to quote, but it's a sensible line to draw.
Cite the Original Source
Another important element of a quote is the source. Citing the source of the quote is extremely important. You can do this in several ways.
- Add the URL to the cite attribute of the blockquote tag, as mentioned above.
- Use a hyperlink in the text to link to the relevant source, with anchor text explaining the source.
- Use a standard AP citation format to cite the source of information that's not a website.
- Attribute the quote to the person making the quote.
Depending on how you received the information you're quoting, you may have to do one or more of these options.
For example, one of my favorite forms of a blog post that I don't write nearly often enough is the quote roundup. Pick a topic and send an email to 10/20/30/50/whatever influencers and big-name personages in the relevant niche. Ask them for a quote or a piece of advice about the topic, or what they think about it, or whatever. For example, I could make a list of 100 SEO professionals and send them all an email asking them where they think audio-format marketing (like podcasting) will go in the next year.

When I get responses back, some of them might link to posts they wrote on the subject, but most will simply answer the question in the email. I can't exactly link to the email, so I'd put the quote – in blockquote tags, of course – with a hyperlink to the homepage of the influencer's site.
This is an interesting hypothetical because I'm technically quoting someone, but that quote isn't taken from another public source. It's not my words, either, so I have to quote it. The fact that its original content means that it's not going to fall afoul of duplicate content penalties, though.
Only Quote Content that Adds to the Post
Part of making sure that your quotes aren't going to damage your site's SEO is making sure your quotes add value to a post you're writing. I'm writing a post about quotations, and I've only added a single quote. In fact, I don't frequently quote others at all. I use a different strategy, which I'll mention at the end of this article.

There's nothing wrong with quoting content from other sites. What you need to do, though, is make sure that the content you're quoting adds value to the article you're writing. What purpose does it serve? Is it useful information? Is it a statement you're going to prove or refute? Is it simply an incidental quote to what you're already writing?
The bar is pretty low here. Relevance is key. As long as the quote you're copying is relevant, you can make it useful somehow.
Add Your Own Content
The key to using quotes, in my opinion (and in the opinion of Matt Cutts from the video up above), is to add more than just quotes to your post.
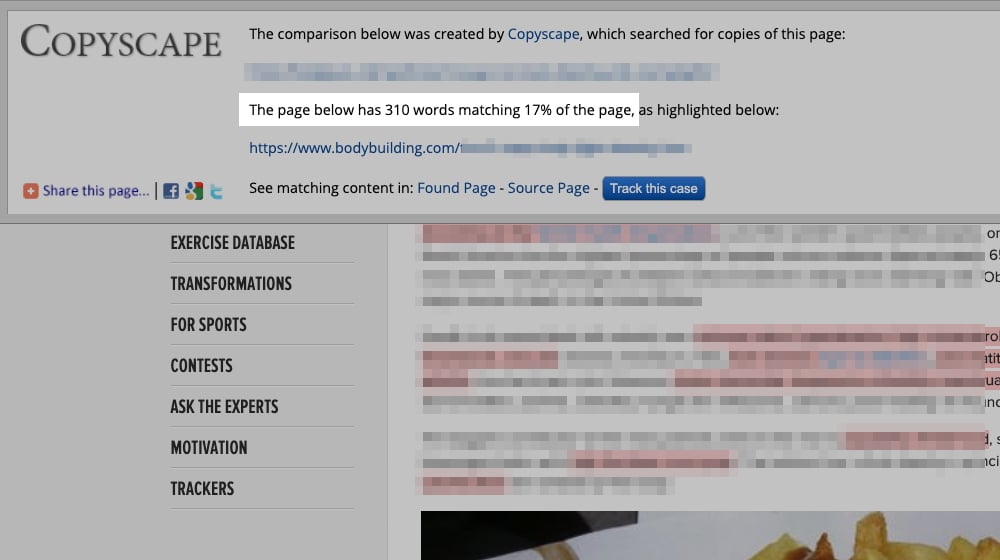
I linked two examples up at the top, a Wishpond post and a HubSpot post, both of which are little more than piles of quotes with no other content. HubSpot did a little better by adding some context to each section of quotes, but the Wishpond post is literally nothing but quotes.
Obviously, since it ranked well in Google, that post isn't performing poorly. On the other hand, it's also nothing special. I found it, read through it, and it brought up a few good points, and cited other sources. There wasn't much value in the content to me beyond that. I suppose I could use it to browse quotes later if I wanted to pull one, but if I did, I'd cite the original source, not the Wishpond copy.
That, to me, is the key to using quotes. Make sure that the majority of your blog post is non-quoted content, and use quotes to accentuate it.
Think of it like icing on a cupcake. The cupcake itself is the main star. The icing – the quote – is just there to accentuate it, decorate it, make it stand out.
Consider Asking Permission
So, here's the thing about quotes; most of the time, you don't need permission to quote it. If the passage is publicly available, you can quote it for whatever purpose you want to quote it. The worst that can usually happen is social backlash if you misinterpret the quote.
In some cases, though, you may want to ask permission to quote someone. For example, if the quote you want to copy is from a private communication, or from a site with a paywall. When the quote isn't publicly available, that's when you might want to obtain permission.
Remember Copyright Exists
Copyright is something I mentioned above. Now, 99% of the time, you're not going to have to worry about copyright when quoting someone. Copyright protects quotations as much as full passages, but it's also a lot more subject to Fair Use. You can read about it here, and another rundown here.

What it basically comes down to is this: a quotation is generally fair use to use in something like a blog post, but using a quotation in product marketing or as part of a product might cause issues. And, of course, if you're "quoting" an entire article from a paywalled website, it doesn't matter how much original content you're surrounding it with, you're still violating that copyright.
Consider Rewriting the Essence of the Quote
I promised my own strategy at the end of the post, and here we are. So what is my strategy? I rewrite it a bit.
Instead of quoting a whole passage, I'll write something like "Andy Crestodina says he's never seen a site penalized for duplicated content outside of specific circumstances", and link that sentence itself to the source of the passage. Even though it's virtually the same information, it's not a direct quote, and thus doesn't need as much specific attention. It still gets the point across, but in my voice, and it still gives you a link to a source.
Is this better than quotes? Maybe, maybe not. It's not going to penalize you, but neither will quotes. It saves me a few seconds over formatting a blockquote tag, but that's not really a selling point. It's just my style. Should you do it too? That's up to you.
What has your experience been with quoting and citing other sources in your articles? Does this clear up any misinformation about duplicate content? Let us know below in our comments area!



 30 Second Summary
30 Second Summary



October 09, 2020
Been following this site for quite a while now and I am really glad I did. Your articles are very helpful James! Keep it up!
October 12, 2020
Hey thanks Ryan! Appreciate the kind words 🙂
November 05, 2020
What I am doing with my blog is I use quotes and rarely cite references in the source section. Do I need to list the source or can I just use the blockquote tags?
November 09, 2020
Hey Dan! I'm a firm believer that Google is smart enough to determine that you're not stealing content when you use the blockquote tags, especially if you're linking to the original post somewhere in the article. The source markup just makes it easier for them to find the original content, but I don't think it will hurt you if you skip or forget this. Using blockquote tags is sufficient in my opinion.
October 03, 2022
That's a relief. I was worried since I do the same thing.
March 26, 2021
Thank you for sharing this. If for example I write an article that is almost the same as the other article but there are some tweaks and additional information, will it be tagged as duplicate? Also, do I need to cite the source?
March 26, 2021
Hey Keith!
I'm not a fan of copying entire articles, but if you do, I would no-index the article. This will tell Google not to index it so that they don't get the wrong idea.
It's also a good idea to cite the source at the bottom of the article.
Something like this would be better suited for your social media profiles, to be honest. I would save your blog for unique content and insights that you or your team wrote.
June 14, 2021
Good stuff, I've always worried about this but that makes perfect sense. Thanks!
June 17, 2021
Hey Dena, happy to help! I'm glad 🙂
August 09, 2021
Hey james.
Very valuable information.
How about sites which only do quotes? Recently I was looking for some new blogging opportunities and saw a lot of scope there. There are many websites that just do quotes.
Like quotesgram, brainyquote, brightdrops... Infact many small websites too and have very good rankings.
I wanted to start a similar thing, but was worried about duplicate content.
Any idea how these websites manage to do?
Thank you
August 11, 2021
Hey Adarsh!
Topic relevance and authority both play a role here.
If the topic is about quotes, and your article primarily has quotes, that makes perfect sense.
If the topic is far more competitive and requires detailed analysis, using many quotes as your article isn't going to achieve the results you were hoping for.
A site's authority can also carry it a long way, even if the content isn't as good. Larger websites can usually get away with publishing thinner content.
Their traffic is likely not entirely from Google either - quotes like these can make for good social media posts. Buzzfeed has very thin content on its site, but the bulk of its traffic comes from social networks, not from search engines.
It's hard to give you specific advice on your website and content without knowing more about it. If your website is about quotes, this advice probably doesn't apply to you in the same way as your average person or company running a blog.
I hope this makes sense!
April 11, 2023
Hello, thank you for very good article. I have some specific question. If I public content where is primary basic prayers like the Lord's Prayer or other, or quote from the Bible, do I need use blackquotes or some other tags for signal to google, that is not duplicate content? Or use for it rel="canonical" ? Thank you for answer 🙂
April 13, 2023
Hey Miroslav,
Blockquotes are what you're looking for!
Your rel="canonical" should point to your blog post (itself), not to any external URL.